What is Doubly Linked List?
In computer science, a doubly linked list is a linked data structure that consists of a set of sequentially linked records called nodes. Each node contains three fields: two link fields (references to the previous and to the next node in the sequence of nodes) and one data field.
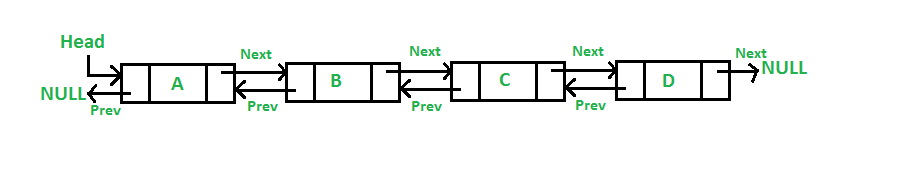
Below are operations on the given DLL:
- Add a node at the front of DLL: The new node is always added before the head of the given Linked List. And the newly added node becomes the new head of DLL & maintaining a global variable for counting the total number of nodes at that time.
- Traversal of a Doubly linked list
-
Insertion of a node: This can be done in three ways:
- At the beginning: The new created node is insert in before the head node and head points to the new node.
- At the end: The new created node is insert at the end of the list and tail points to the new node.
-
At a given position: Traverse the given DLL to that position(let the node be X) then do the following:
- Change the next pointer of new Node to the next pointer of Node X.
- Change the prev pointer of next Node of Node X to the new Node.
- Change the next pointer of node X to new Node.
- Change the prev pointer of new Node to the Node X.
-
Deletion of a node: This can be done in three ways:
- At the beginning: Move head to the next node to delete the node at the beginning and make previous pointer of current head to NULL .
- At the last: Move tail to the previous node to delete the node at the end and make next pointer of tail node to NULL.
-
At a given position: Let the prev node of Node at position pos be Node X and next node be Node Y, then do the following:
- Change the next pointer of Node X to Node Y.
- Change the previous pointer of Node Y to Node X.
Following is a representation of a DLL node:
public class DLL {
// Head of list
Node head;
// Doubly Linked list Node
class Node {
int data;
Node prev;
Node next;
// Constructor to create a new node
// next and prev is by default initialized as null
Node(int d) {
data = d;
}
}
}
Delete a node in a Doubly Linked List
public class DLL {
Node head; // head of list
/* Doubly Linked list Node*/
class Node {
int data;
Node prev;
Node next;
// Constructor to create a new node
// next and prev is by default initialized
// as null
Node(int d) { data = d;
}
}
// Adding a node at the front of the list
public void push(int new_data)
{
// 1. allocate node
// 2. put in the data
Node new_Node = new Node(new_data);
// 3. Make next of new node as head
// and previous as NULL
new_Node.next = head;
new_Node.prev = null;
// 4. change prev of head node to new node
if (head != null)
head.prev = new_Node;
// 5. move the head to point to the new node
head = new_Node;
}
// This function prints contents of linked list
// starting from the given node
public void printlist(Node node)
{
Node last = null;
while (node != null) {
System.out.print(node.data + " ");
last = node;
node = node.next;
}
System.out.println();
}
// Function to delete a node in a Doubly Linked List.
// head_ref --> pointer to head node pointer.
// del --> data of node to be deleted.
void deleteNode(Node del)
{
// Base case
if (head == null || del == null) {
return;
}
// If node to be deleted is head node
if (head == del) {
head = del.next;
}
// Change next only if node to be deleted
// is NOT the last node
if (del.next != null) {
del.next.prev = del.prev;
}
// Change prev only if node to be deleted
// is NOT the first node
if (del.prev != null) {
del.prev.next = del.next;
}
// Finally, free the memory occupied by del
return;
}
// Driver Code
public static void main(String[] args)
{
// Start with the empty list
DLL dll = new DLL();
// Insert 2. So linked list becomes 2->NULL
dll.push(2);
// Insert 4. So linked list becomes 4->2->NULL
dll.push(4);
// Insert 8. So linked list becomes 8->4->2->NULL
dll.push(8);
// Insert 10. So linked list becomes
// 10->8->4->2->NULL
dll.push(10);
System.out.print("Original Linked list ");
dll.printlist(dll.head);
dll.deleteNode(dll.head); /*delete first node*/
dll.deleteNode(dll.head.next); /*delete middle node*/
dll.deleteNode(dll.head.next); /*delete last node*/
System.out.print(
"\nModified Linked list ");
dll.printlist(dll.head);
}
}
Output:
Original Linked list 10 8 4 2
Modified Linked list 8
Time Complexity: O(1).
traversal of the linked list is not required so the time complexity is constant.
Auxiliary Space: O(1).
As no extra space is required, so the space complexity is constant.
Insertion in Circular Doubly Linked List:
-
Insertion at the end:
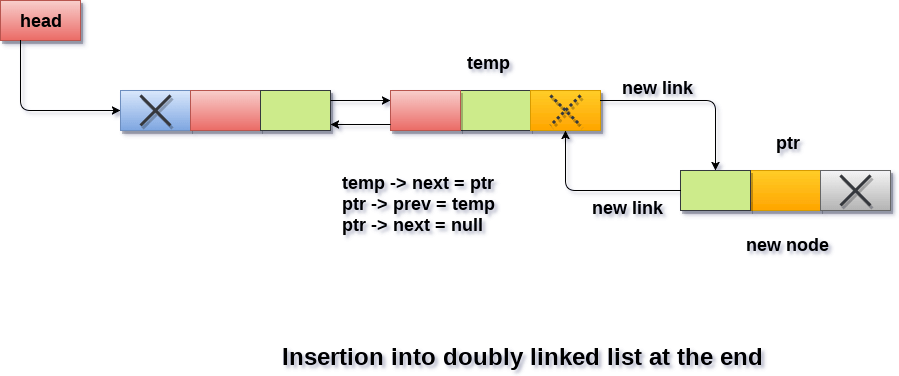
class PrepInsta
{
//Constitiute a node of the doubly linked list
class Node{
int data;
Node prev;
Node next;
public Node(int data) {
this.data = data;
}
}
// Function to traverse and print the linked list
public void display() {
Node temp = head;
while (temp != null) {
System.out.print(temp.data + "–>");
// Set temp to point to the next node
temp = temp.next;
}
System.out.println("END");
}
//Constitiute the head and tail of the doubly linked list
Node head, tail = null;
//appendAtEnd function will add a node to the end of the list
public void appendAtEnd(int data) {
//Create a new node
Node newNode = new Node(data);
//Check if the list is empty
if(head == null) {
//Both head and tail will point towards the newNode
head = tail = newNode;
//head's previous will point towards null
head.prev = null;
//tail's next will point towards null, as it is the last node of the list
tail.next = null;
}
//Append newNode as new tail of the list
else {
//newNode will be added after tail such that tail's next will point to newNode
tail.next = newNode;
//newNode's previous will point to tail
newNode.prev = tail;
//newNode will become new tail
tail = newNode;
//As it is last node, tail's next will point to null
tail.next = null;
}
}
//print() will print the nodes of the doubly linked list
void print() {
//Node current will point to head
Node curr = head;
if(head == null) {
System.out.println("List is empty");
return;
}
System.out.println("Appending a node to the end of the list: ");
while(curr != null)
{
//Prints each node by increasing order of the pointer
System.out.print(curr.data + " ");
curr = curr.next;
}
System.out.println();
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
PrepIdList = new PrepInsta();
//Appending 10 to the list
dList.appendAtEnd(10);
dList.print();
//Appending 20 to the list
dList.appendAtEnd(20);
dList.print();
//Appending 30 to the list
dList.appendAtEnd(30);
dList.print();
//Appending 40 to the list
dList.appendAtEnd(40);
dList.print();
//Appending 50 to the list
dList.appendAtEnd(50);
dList.print();
}
}
-
Insertion at the front:
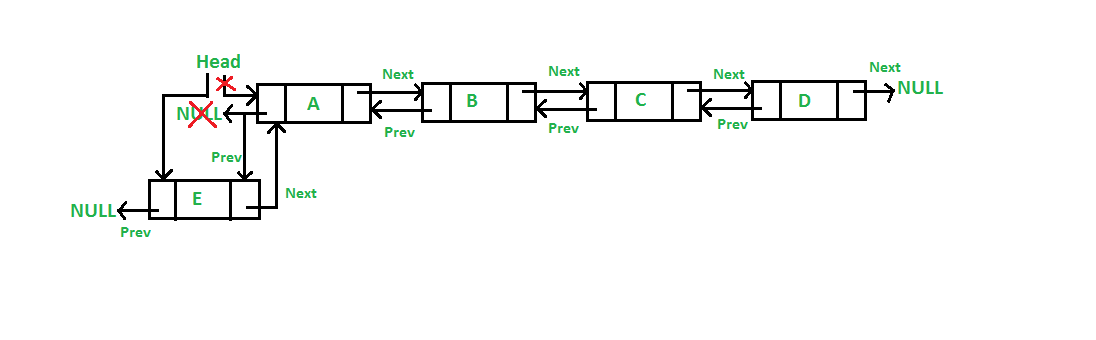
public class InsertStart {
//Represent a node of the doubly linked list
class Node{
int data;
Node previous;
Node next;
public Node(int data) {
this.data = data;
}
}
//Represent the head and tail of the doubly linked list
Node head, tail = null;
//addAtStart() will add a node to the starting of the list
public void addAtStart(int data) {
//Create a new node
Node newNode = new Node(data);
//If list is empty
if(head == null) {
//Both head and tail will point to newNode
head = tail = newNode;
//head's previous will point to null
head.previous = null;
//tail's next will point to null, as it is the last node of the list
tail.next = null;
}
//Add newNode as new head of the list
else {
//head's previous node will be newNode
head.previous = newNode;
//newNode's next node will be head
newNode.next = head;
//newNode's previous will point to null
newNode.previous = null;
//newNode will become new head
head = newNode;
}
}
//display() will print out the nodes of the list
public void display() {
//Node current will point to head
Node current = head;
if(head == null) {
System.out.println("List is empty");
return;
}
System.out.println("Adding a node to the start of the list: ");
while(current != null) {
//Prints each node by incrementing the pointer.
System.out.print(current.data + " ");
current = current.next;
} System.out.println();
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
InsertStart dList = new InsertStart();
//Adding 1 to the list
dList.addAtStart(1);
dList.display();
//Adding 2 to the list
dList.addAtStart(2);
dList.display();
//Adding 3 to the list
dList.addAtStart(3);
dList.display();
//Adding 4 to the list
dList.addAtStart(4);
dList.display();
//Adding 5 to the list
dList.addAtStart(5);
dList.display();
}
}
-
Insertion at any position:
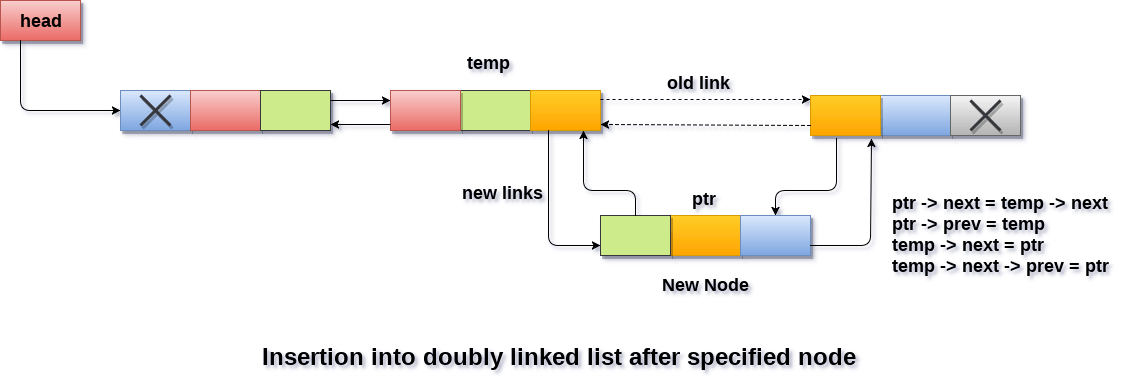
//node structure
class Node {
int data;
Node next;
Node prev;
};
class LinkedList {
Node head;
LinkedList(){
head = null;
}
//Add new element at the end of the list
void push_back(int newElement)
{
Node newNode = new Node();
newNode.data = newElement;
newNode.next = null;
newNode.prev = null;
if(head == null) {
head = newNode;
}
else {
Node temp = new Node();
temp = head;
while(temp.next != null)
temp = temp.next;
temp.next = newNode;
newNode.prev = temp;
}
}
//Inserts a new element at the given position
void push_at(int newElement, int position) {
Node newNode = new Node();
newNode.data = newElement;
newNode.next = null;
newNode.prev = null;
if(position < 1) {
System.out.print("\nposition should be >= 1.");
}
else if (position == 1) {
newNode.next = head;
head.prev = newNode;
head = newNode;
}
else {
Node temp = new Node();
temp = head;
for(int i = 1; i < position-1; i++) {
if(temp != null) {
temp = temp.next;
}
}
if(temp != null) {
newNode.next = temp.next;
newNode.prev = temp;
temp.next = newNode;
if(newNode.next != null)
newNode.next.prev = newNode;
}
else {
System.out.print("\nThe previous node is null.");
}
}
}
//display the content of the list
void PrintList() {
Node temp = new Node();
temp = this.head;
if(temp != null) {
System.out.print("The list contains: ");
while(temp != null) {
System.out.print(temp.data + " ");
temp = temp.next;
}
System.out.println();
}
else {
System.out.println("The list is empty.");
}
}
};
// test the code
public class Implementation {
public static void main(String[] args) {
LinkedList MyList = new LinkedList();
//Add three elements in the list.
MyList.push_back(10);
MyList.push_back(20);
MyList.push_back(30);
MyList.PrintList();
//Insert an element at position 2
MyList.push_at(100, 2);
MyList.PrintList();
//Insert an element at position 1 MyList.push_at(200, 1);
MyList.PrintList();
}
}
Time Complexity: O(1).
traversal of the linked list is not required so the time complexity is constant.
Auxiliary Space: O(1).
As no extra space is required, so the space complexity is constant.
Home